Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition (CPPD)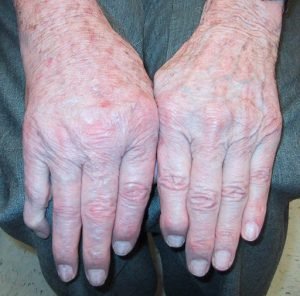
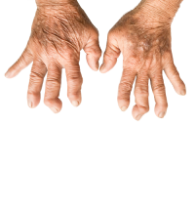
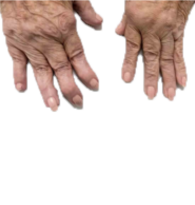
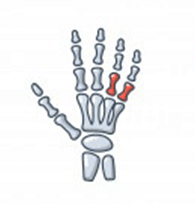
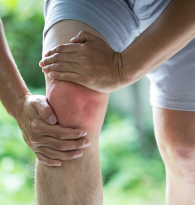
Pseudogout (or “false gout”) is a form of arthritis that results from deposits of calcium pyrophosphate crystals, hence its new name of calcium Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease or CPPD. It commonly affects the knees and wrists.
In some joints causes pain, stiffness, tenderness, redness, warmth, and swelling. It usually affects one joint at a time, but may often affect several joints at once.
Symptoms:
• Sudden, intense joint pain
• Swollen joint that is warm and tender to touch
• Red skin involving the affected joint
Treatment
No treatment is available to dissolve the crystal deposits. For patients who have acute attacks, the doctor may prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are commonly called NSAIDs. NSAIDs, like indomethacin and naproxen, treat pain and swelling during severe attacks.