Vasculitis
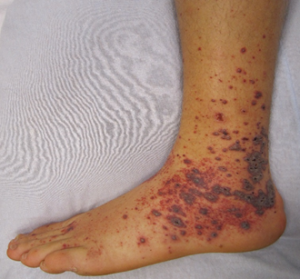
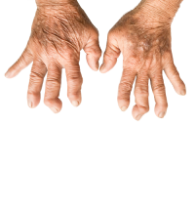
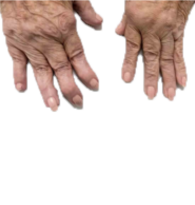
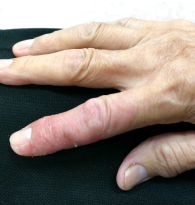
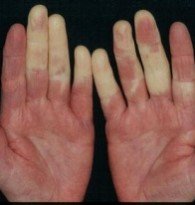
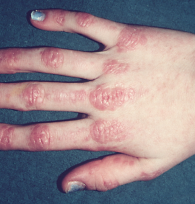
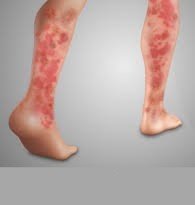
Vasculitis is a blood vessel inflammation. This happens when the body’s immune system wrongly targets the blood vessel. It may occur due to an infection, a drug, or another disease. Sometimes, the cause is not understood.
Vasculitis can affect arteries, capillaries and veins. Arteries are vessels which take blood from the heart to the organs of the body. Veins are the vessels that bring back blood to the heart. Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that bind small arteries and veins together.
When a blood vessel becomes inflamed, it can
• Narrow, making it more difficult for blood to get through
• Close off completely so that blood can’t get through
• Stretch and weaken so much that it bulges. The bulge is called an aneurysm. If it bursts, it can cause dangerous bleeding inside the body.
Symptoms of vasculitis can vary, but usually include fever, swelling and a general sense of feeling ill. The main goal of treatment is to stop the inflammation. Steroids and other medicines to stop inflammation are often helpful.
Treatment of vasculitis depends entirely upon diagnosis and the affected organs.